Well, Microsoft finally did it. Sort of. The new Windows File Recovery app isn’t like the average point-and-click app. No, it’s a Command Line Interface (CLI) utility. So you need to get comfortable working in the Command window.
Where Can I Get Windows File Recovery?
Windows File Recovery is available right now in the Microsoft Store app on your Windows 10 computer. You can go to download Windows File Recovery from the online Microsoft Store, too. The question is, do you really want to? Windows File Recovery requires Windows 10 2004 to work, at the very least. That version was released on May 27th, 2020. So you might need to update Windows. You can get the upgrade here: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/software-download/windows10
What Can I Do With Windows File Recovery?
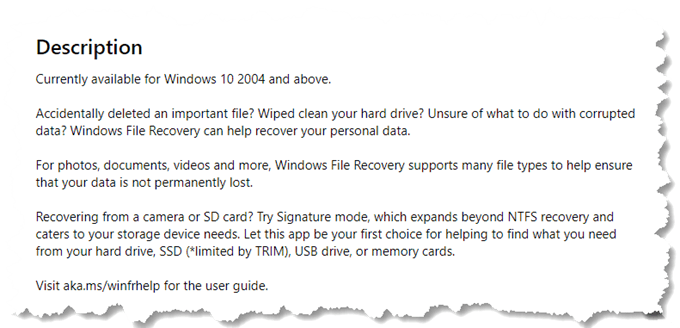
If you’re reading Microsoft’s own press, it sounds like you can do just about anything with Windows File Recovery. They say that you can recover ordinary deleted files, resurrect wiped hard drives, and fix corrupted data. Sounds good. They go on to say that it can recover files from SSD (TRIM will limit that), cameras, SD Cards, and USB drives. That’s impressive. Microsoft tells us Windows File Recovery also works on a broad variety of file systems. It supports NTFS, FAT, exFAT, and ReFS file systems.
How Do I Use Windows File Recovery?
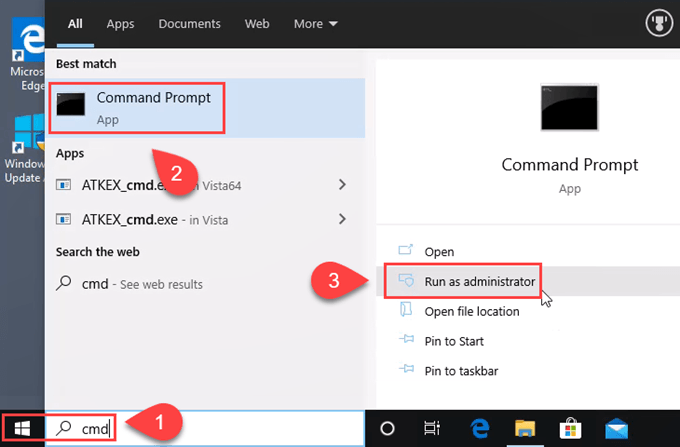
Open the Command window as Administrator.
Note that you cannot recover a file from one disk partition to the same partition. For example, you can’t recover a file from your C: drive to your C: drive. Recovering from your C: drive to your F: drive, if you have one, will work.
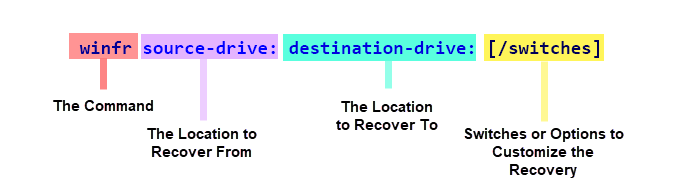
The following is the basic syntax of a Windows File Recovery command:
To recover deleted files from your desktop to your F: drive, your command would look like this:
winfr C: F: /n Users\User\Desktop\ where
What Are The Modes of Windows File Recovery?
The three mods for the Windows File Recovery command include: Default – The basic search that uses the Master File Table (MFT) to find the files. Default is best for most situations, soon after the file was deleted. Segment – In an NTFS drive file information is stored in segments that are like a summary of the file’s information. Segment mode is best for files that were deleted a while ago, or if the disk was formatted or corrupted. Signature – Used if your filesystem is FAT, exFAT, or ReFS. You can try this mode on NTFS if Segment mode doesn’t work.
What Are The Windows File Recovery Switches?
Available switches you can use with the Windows File Recovery command include:
/r – Segment mode.
/n
Is Windows File Recovery Worth Using?
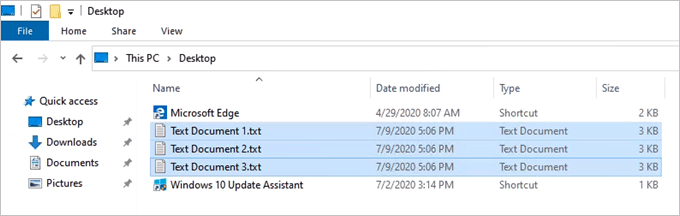
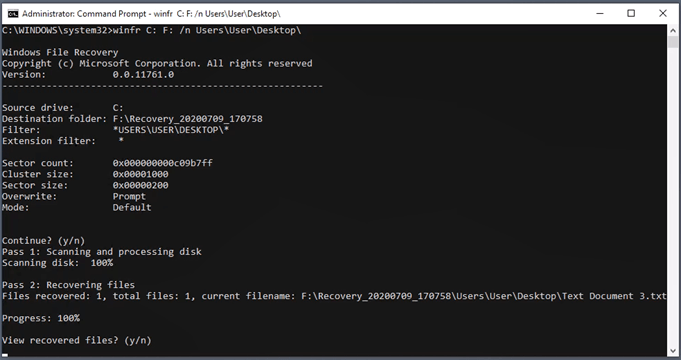
It’s up to you to decide whether Windows File Recovery is best for your situation. However, in our testing, we created 3 plain text files filled with lorem ipsum text and deleted them. Then they were removed from the Recycle Bin as well. Finally,Then we used the recovery command as seen above to try to recover the files. Windows File Recovery wasn’t able to recover all 3 simple text files reliably. After 5 tries, it only recovered all 3 files twice. Below is an example of when it only recovered one file. Our test was done on a fresh install of Windows 10 2004, with no additional programs installed and no other user files. It was basically a new Windows computer. If you don’t have access to another file recovery program and the computer has Windows File Recovery already on it, it might be worth using first. If your usual file recovery app cannot recover the files, then Windows File Recovery may be worth trying as a backup solution.
Then Why Is Windows File Recovery Big News?
There’s only 2 real reasons why Windows File Recovery was big news. It’s partly because it’s shocking that Microsoft even bothered to create this after a couple of decades. It’s also partly because it plants a tiny seed of hope that Microsoft will continue to develop the utility and maybe create a full-blown, unbeatable file recovery tool. Time will tell.